Free Resources
Free Resources
Social and Emotional Learning
The Significant Seven
Emotional maturity is the ability to remain composed and controlled in the turbulent world of other people and unpredictable events. Social maturity is related to our own self-management, the ability to connect with other people and respond to them while maintaining our own integrity and individuality.
To manage self in these ways, we need to know and understand self. That sounds like a simple formula, but because we are complex creatures it is not. There is a lot to learn if we are to thrive, maintain our integrity as individuals and be resilient in a challenging and uncertain world.
The following are my 'Significant Seven': areas in which we can develop our own self-understanding and our compassionate awareness of other people.
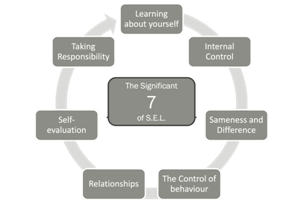
Each of the seven areas of development is linked to knowledge, skills and strategies that will help in growing your own social and emotional development and in helping others to develop in this area.
1. Learning about yourself: How your mind works
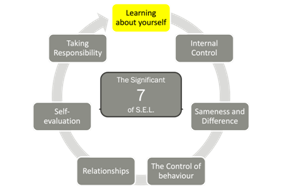
Learning about yourself
- How your mind works.
- Needs and how we learn to satisfy them.
- Understanding your Quality World – unique to every person.
- Why we do what we do: motivation.
2. We are Internally Controlled
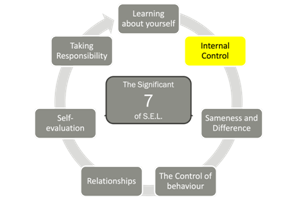
We are internally controlled:
- We have a control system.
- Our control system is internal – it is inside us.
- We Can control our own behaviors to get what we want.
- We can't control other people.
- Because Freedom (Autonomy) is an important need we resist coercion
3. Ways in which we are the same: Ways we are different
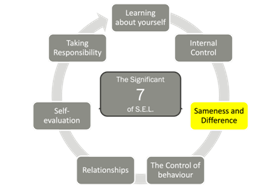
Sameness and Difference
- We have the samegeneric needs.
- We satisfy our needs differently.
- We have the same kind of control system.
- We have differentwants in our Quality World.
- We have different Perceptions.
4. How we control our behaviour
How we control our behaviour
- Thinking.
- Acting.
- Feeling.
- Physiology.
- Behavioural repertoire
- Creating new behaviours
5. Creating and maintaining relationships
Creating and maintaining relationships
- How we connect and disconnect with others
- Influence, not control
- Mending relationships
6. Self-evaluation
Self-evaluation
- The difference between external and internal locus of control.
- Nobody is really controlled by other people but all of us can choose to do what other people want.
- Preferring what other people want towhat is need satisfying for us, is unhealthy.
- Evaluating self is important.
7. Taking Responsibility
Taking Responsibility
- Definition of responsibility.
- Never blame, complain or make excuses.
- Managing Self
- Stop Tool